ROR2 Primary Antibody
Item Information
Catalog #
Size
Price
Description
The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor protein tyrosine kinase and type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the ROR subfamily of cell surface receptors. The protein may be involved in the early formation of the chondrocytes and may be required for cartilage and growth plate development. Mutations in this gene can cause brachydactyly type B, a skeletal disorder characterized by hypoplasia/aplasia of distal phalanges and nails. In addition, mutations in this gene can cause the autosomal recessive form of Robinow syndrome, which is characterized by skeletal dysplasia with generalized limb bone shortening, segmental defects of the spine, brachydactyly, and a dysmorphic facial appearance.
Product Overview
Entrez GenelD
4920
Aliases
BDB; BDB1; NTRKR2
Clone#
6F2D10
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Species Reactivity
Human
Immunogen
Purified recombinant fragment of human ROR2 (AA: 59-155) expressed in E. Coli.
Formulation
Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide.
Storage
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Product Applications
WB (Western Blot)
1/500 - 1/2000
FCM (Flow Cytometry)
1/200 - 1/400
ELISA
1/10000
References
1. Int J Cancer. 2013 Aug 15;133(4):779-87.
2. Mol Cancer. 2010 Jun 30;9:170.
2. Mol Cancer. 2010 Jun 30;9:170.
Product Image
Western Blot

Figure 1: Western blot analysis using ROR2 mAb against human ROR2 (AA: 59-155) recombinant protein. (Expected MW is 36.8 kDa)
Western Blot

Figure 2: Western blot analysis using ROR2 mAb against HEK293 (1) and ROR2 (AA: 59-155)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.
Flow cytometric
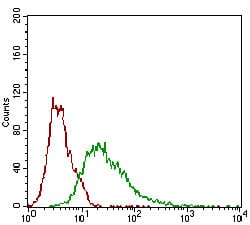
Figure 3: Flow cytometric analysis of Hela cells using ROR2 mouse mAb (green) and negative control (red).
Elisa

Black line: Control Antigen (100 ng); Purple line: Antigen(10ng); Blue line: Antigen (50 ng); Red line: Antigen (100 ng);
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

