RAN Primary Antibody
Item Information
Catalog #
Size
Price
Description
RAN (ras-related nuclear protein) is a small GTP binding protein belonging to the RAS superfamily that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The RAN protein is also involved in control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. Nuclear localization of RAN requires the presence of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Mutations in RAN disrupt DNA synthesis. Because of its many functions, it is likely that RAN interacts with several other proteins. RAN regulates formation and organization of the microtubule network independently of its role in the nucleus-cytosol exchange of macromolecules. RAN could be a key signaling molecule regulating microtubule polymerization during mitosis. RCC1 generates a high local concentration of RAN-GTP around chromatin which, in turn, induces the local nucleation of microtubules. RAN is an androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that binds differentially with different lengths of polyglutamine within the androgen receptor. Polyglutamine repeat expansion in the AR is linked to Kennedy's disease (X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy). RAN coactivation of the AR diminishes with polyglutamine expansion within the AR, and this weak coactivation may lead to partial androgen insensitivity during the development of Kennedy's disease.
Product Overview
Entrez GenelD
5901
Aliases
TC4; Gsp1; ARA24
Clone#
8D1H12
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Species Reactivity
Human, Monkey, Rat
Immunogen
Purified recombinant fragment of human RAN (AA: 1-216) expressed in E. Coli.
Formulation
Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide
Storage
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Product Applications
WB (Western Blot)
1/500 - 1/2000
IHC_P(Immunohistochemistry)
1/200 - 1/1000
FCM (Flow Cytometry)
1/200 - 1/400
ELISA
1/10000
References
1.Int J Clin Oncol. 2013 Oct;18(5):856-63.
2.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 15;18(2):380-91.
2.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 15;18(2):380-91.
Product Image
Elisa
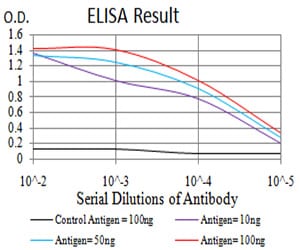
Figure 1: Black line: Control Antigen (100 ng);Purple line: Antigen (10ng); Blue line: Antigen (50 ng); Red line:Antigen (100 ng)
Western Blot
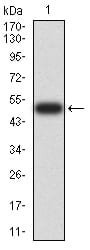
Figure 2:Western blot analysis using RAN mAb against human RAN (AA: 1-216) recombinant protein. (Expected MW is 50.4 kDa)
Western Blot

Figure 3:Western blot analysis using RAN mAb against HEK293 (1) and RAN (AA: 1-216)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.
Western Blot
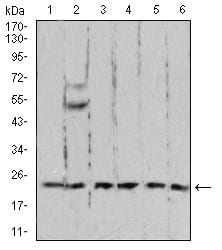
Figure 4:Western blot analysis using RAN mouse mAb against A431 (1), C6 (2), Jurkat (3), Hela (4), COS7 (5), and Jurkat (6) cell lysate.
Flow cytometric
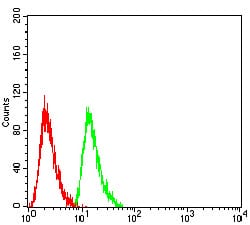
Figure 5:Flow cytometric analysis of Hela cells using RAN mouse mAb (green) and negative control (red).
Immunohistochemical analysis
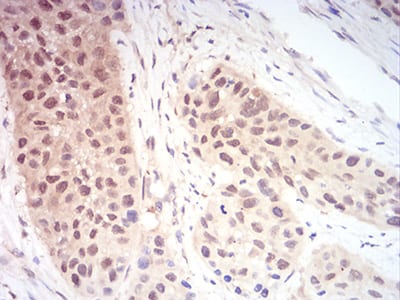
Figure 6:Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded esophageal cancer tissues using RAN mouse mAb with DAB staining.
Immunohistochemical analysis
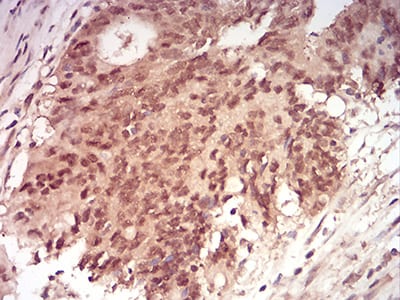
Figure 7:Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rectum cancer tissues using RAN mouse mAb with DAB staining.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

