KID Primary Antibody
Item Information
Catalog #
Size
Price
Description
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of kinesin-like protein family. This family of proteins are microtubule-dependent molecular motors that transport organelles within cells and move chromosomes during cell division. The C-terminal half of this protein has been shown to bind DNA. Studies with the Xenopus homolog suggests its essential role in metaphase chromosome alignment and maintenance.
Product Overview
Entrez GenelD
3835
Aliases
KIF22; KID; OBP; KNSL4; OBP-1; OBP-2; A-328A3.2
Clone#
5F3
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Species Reactivity
Human
Immunogen
Purified recombinant fragment of human KID expressed in E. Coli.
Formulation
Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide.
Storage
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Product Applications
WB (Western Blot)
1/500 - 1/2000
IHC_P(Immunohistochemistry)
1/200 - 1/1000
ELISA
1/10000
References
1. Cell. 2008 Mar 7;132(5):771-82.
2. Retrovirology. 2009 May 19;6:47.
2. Retrovirology. 2009 May 19;6:47.
Product Image
Western Blot

Figure 1: Western blot analysis using KID mAb against human KID (AA: 225-419) recombinant protein. (Expected MW is 47 kDa)
Western Blot

Figure 2: Western blot analysis using KID mouse mAb against MCF-7 (1) and Hela (2) cell lysate.
Immunohistochemical analysis

Figure 3: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded cervical cancer tissues using KID mouse mAb with DAB staining.
Immunohistochemical analysis

Figure 4: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rectum cancer tissues using KID mouse mAb with DAB staining.
Elisa
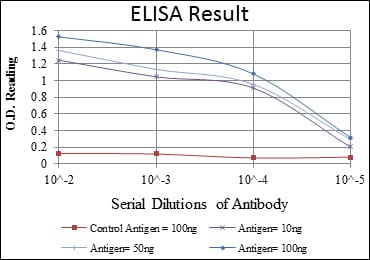
Red: Control Antigen (100ng); Purple: Antigen (10ng); Green: Antigen (50ng); Blue: Antigen (100ng);
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

